TRIANGLE PROPORTIONALITY THEOREM
Definition Of Triangle Proportionality Theorem
Triangle Proportionality Theorem states that a line drawn parallel to any of the sides of a triangle divides the other two sides proportionally.
Example of Triangle Proportionality Theorem
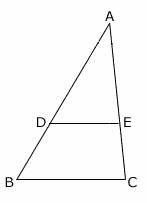
In the given triangle ABC, BC is the base of the triangle.
DE is drawn parallel to BC and it intersects the other two sides AB and AC at D and E respectively.
Here, 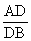 =
= 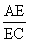 .
.
This is called triangle proportionality theorem.
Video Examples: Key Stage 1 Maths: Addition
Solved Example on Triangle Proportionality Theorem
Ques: QP || BC. If AQ = 3 cm, PC = 4 cm, QB = 11 cm, and BC = 12 cm, then find the length of AP rounded to the nearest decimal.
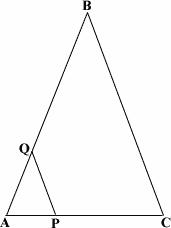
Choices:
A. 2.59 cm
B. 1.09 cm
C. 2.09 cm
D. 1.59 cm
Correct Answer: B
Solution:
Step 1: A line drawn parallel to any of the sides of a triangle divides the other two sides proportionally.
Step 2: 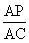 =
= 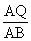 [Proportionality Theorem.]
[Proportionality Theorem.]
Step 3:  [Substitute the values.]
[Substitute the values.]
Step 4: 14(AP) = 3(AP) + 12 [Cross multiplication.]
Step 5: 11(AP) = 12 [Simplify.]
Step 6: AP = 1.09 [Divide by 11 on both sides.]
Step 7: The length of AP is 1.09 cm.
Quick Summary
- A line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides.
- The parallel line divides the intersected sides proportionally.
⚠️ Common Mistakes
- Incorrectly setting up the proportion.
- Confusing the segments of the sides.
🌍 Real-World Uses
- Architecture: Calculating proportional lengths in roof trusses to ensure structural stability.
- Mapmaking: Determining distances on a map based on proportional relationships to actual distances on the ground.
- Carpentry: Dividing a piece of wood into proportional segments for decorative trim or framing.
📋 Standards Alignment
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.B.4
🔗 Related Links
🍎 Teacher Insights
Use visual aids and real-world examples to demonstrate the theorem. Emphasize the importance of correctly identifying corresponding segments when setting up proportions.🎓 Prerequisites
- Similar Triangles
- Ratios
- Proportions
Check Your Knowledge
Q1: In triangle ABC, line DE is parallel to BC. If AD = 4, DB = 6, and AE = 5, what is the length of EC?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What does it mean for sides to be divided proportionally?
A: It means the ratio of the segments on one side is equal to the ratio of the segments on the other side.
Q: Can this theorem be used to prove lines are parallel?
A: Yes, the converse of the theorem can be used to prove that a line is parallel to one side of a triangle if it divides the other two sides proportionally.