ONE TO ONE FUNCTION
Definition Of One To One Function
A function is said to be a One-to-One Function, if for each element of range, there is a unique domain.
More About One to One Function
One-to-one function satisfies both vertical line test as well as horizontal line test.
One-to-one function is also called as injective function.
Example of One to One Function
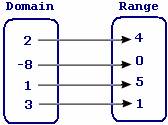
In the given figure, every element of range has unique domain.
So, the given function is one-to-one function.
Video Examples: One-to-one Functions
Solved Example on One to One Function
Ques: Let A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {a, b, c, d}. Which of the following is a one-to-one function?
Choices:
A. {(1, a), (2, c), (3, a)}
B. {(1, b), (2, d), (3, a)}
C. {(1, a), (2, a), (3, a)}
D. {(1, c), (2, b), (1, a), (3, d)}
Correct Answer: B
Solution:
Step 1: Here, option B satisfies the condition for one-to-one function, as the elements of the range set B are mapped to unique element in the domain set A and the mapping can be shown as:
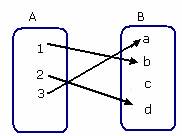
Step 2: Hence Option B satisfies the condition for a function to be one-to-one.
Quick Summary
- For each element of the range, there is a unique element in the domain.
- Satisfies both vertical and horizontal line tests.
- Also called an injective function.
⚠️ Common Mistakes
- Confusing one-to-one with other types of functions (e.g., onto).
- Incorrectly applying the horizontal line test.
🌍 Real-World Uses
- Data encryption: Each plaintext character is mapped to a unique ciphertext character, allowing for decryption.
- Assigning social security numbers: Each person is assigned a unique number to avoid identity conflicts.
- Barcodes on products: Each barcode uniquely identifies a specific product in inventory management.
🔗 Related Links
🍎 Teacher Insights
Use visual aids like graphs to demonstrate the horizontal line test. Emphasize the uniqueness of the mapping from range to domain.🎓 Prerequisites
- Functions
- Domain
- Range
- Vertical Line Test
Check Your Knowledge
Q1: Which of the following relations is a one-to-one function if A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {a, b, c, d}?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I determine if a function is one-to-one?
A: Check if it satisfies the horizontal line test. If any horizontal line intersects the graph more than once, it is not one-to-one.
Q: What is the difference between a one-to-one function and an onto function?
A: A one-to-one function has a unique domain element for each range element. An onto function has its range equal to its codomain, meaning every possible output is actually achieved.