ISOMETRY
Definition Of Isometry
An isometry is a transformation in which the original figure and its image are congruent.
More About Isometry
Isometry is invariant with respect to distance. That is, in an isometry, the distance between any two points in the original figure is the same as the distance between their corresponding images in the transformed figure (image).
Reflections, rotations, translations are isometries.
Dilation is not an isometry.
Video Examples: Regular and Isometry
Example of Isometry
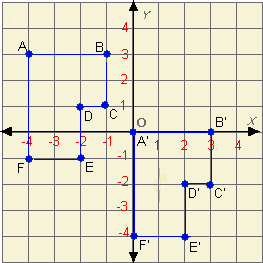
The figure shows a translation, an isometry.
An irregular polygon ABCDE is translated to A'B'C'D'E'.
Notice that the distance between A and B is the same as the distance between their image A' and B'.
Solved Example on Isometry
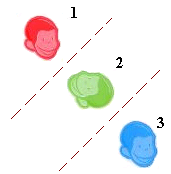
Ques: What isometry maps figure 1 to figure 3?
Choices:
A. reflection
B. translation
C. rotation
D. none of these
Correct Answer: B
Solution:
Step 1: An isometry is a transformation in which the original figure and its image are congruent.
Step 2: A reflection flips the figure across a line. The new figure is a mirror image of the original figure.
Step 3: Figure 2 is a reflection of Figure 1 and Figure 3 is a reflection of Figure 2.
Step 4: A translation is the composition of two reflections in parallel lines.
Step 5: So, the isometry that maps Figure 1 to Figure 3 is a translation.
Quick Summary
- Isometry preserves distance.
- Reflections, rotations, and translations are isometries.
- Dilation is not an isometry.
⚠️ Common Mistakes
- Confusing isometries with other transformations that don't preserve distance (e.g., dilations).
- Assuming all transformations are isometries.
🌍 Real-World Uses
- Computer graphics utilize isometric transformations to rotate and reposition 3D models without distorting their shapes, ensuring objects appear realistic from different viewpoints.
- In architecture, isometric projections are used to create 2D representations of 3D buildings and spaces, preserving proportions and spatial relationships for design and planning.
- Medical imaging, such as MRI and CT scans, relies on isometric transformations to reconstruct 3D images from 2D slices without altering the size or shape of organs or tissues.
📋 Standards Alignment
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.2CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.B.6
🔗 Related Links
🍎 Teacher Insights
Use manipulatives or dynamic geometry software to demonstrate how isometries preserve distance and congruence. Emphasize the difference between isometries and transformations that change size or shape.🎓 Prerequisites
- Congruence
- Transformations
- Reflections
- Rotations
- Translations
Check Your Knowledge
Q1: Which of the following transformations is NOT an isometry?
Q2: If a figure undergoes an isometry, what is true about the original figure and its image?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What transformations are isometries?
A: Reflections, rotations, and translations are isometries.
Q: Does an isometry change the size or shape of a figure?
A: No, isometries only change the position or orientation of a figure; the size and shape remain the same.