POSTULATE
Definition Of Postulate
Postulate is a true statement, which does not require to be proved.
More About Postulate
Postulate is used to derive the other logical statements to solve a problem.
Postulates are also called as axioms.
Example of Postulate
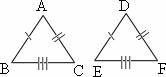
To prove that these triangles are congruent, we use SSS postulate, as the corresponding sides of both the triangles are equal.
Video Examples: The five postulates of Euclidean Geometry
Solved Example on Postulate
Ques: State the postulate or theorem you would use to prove that ∠1 and ∠2 are congruent.
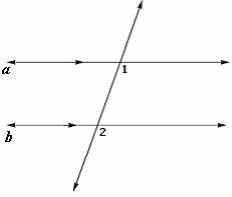
Choices:
A. corresponding angles postulate
B. converse of corresponding angles postulate
C. alternate angles are congruent
D. adjacent angles are congruent
Correct Answer: A
Solution:
Step 1: ∠1 and ∠2 corresponding angles.
Step 2: Since the lines a and b are parallel, ∠1 and ∠2 are congruent. [Corresponding angles postulate.]
Step 3: So, corresponding angles postulate is used to prove that ∠1 and ∠2 are congruent.
Quick Summary
- Postulates are true statements that do not require proof.
- They are also called axioms.
- Postulates are used to derive other logical statements.
- The SSS postulate is used to prove triangle congruence.
⚠️ Common Mistakes
- Confusing postulates with theorems (theorems require proof).
- Assuming a statement is a postulate without proper justification.
🌍 Real-World Uses
- Architecture: Using geometric postulates to ensure the stability and accuracy of building designs.
- Navigation: Applying postulates about lines and angles in GPS systems and mapmaking for accurate positioning.
- Computer Graphics: Utilizing geometric postulates in rendering 3D models and creating realistic visual effects.
📋 Standards Alignment
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.1CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.B.7CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.C.10
🔗 Related Links
🍎 Teacher Insights
Emphasize the difference between postulates and theorems. Use visual aids and real-world examples to illustrate the application of different postulates. Encourage students to question the validity of statements and determine whether they require proof or can be accepted as postulates.🎓 Prerequisites
- Basic geometric shapes
- Understanding of logical statements
- Concept of congruence
Check Your Knowledge
Q1: Which of the following is a postulate?
Q2: What is another name for a postulate?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between a postulate and a theorem?
A: A postulate is assumed to be true without proof, while a theorem requires a proof based on previously established postulates or theorems.
Q: Are postulates universal, or can they vary?
A: While some postulates are universally accepted, different axiomatic systems can exist, each based on its own set of postulates. Euclidean Geometry is based on a set of postulates different from, for example, non-Euclidean geometries.