HYPERBOLA
Definition Of Hyperbola
Hyperbola is a conic section in which difference of distances of all the points from two fixed points (called `foci`) is constant.
More About Hyperbola
The general equation for hyperbola is 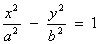 .
.
The eccentricity (e) of a hyperbola is always greater than 1, e > 1.
The slope of asymptotes for both horizontal and vertical hyperbola is 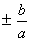 .
.
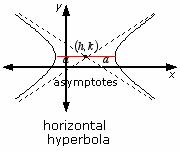
The equation for the horizontal hyperbola is 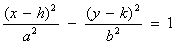 .
.
Video Examples: Hyperbola
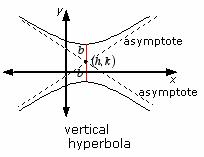
The equation for the vertical hyperbola is 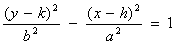 .
.
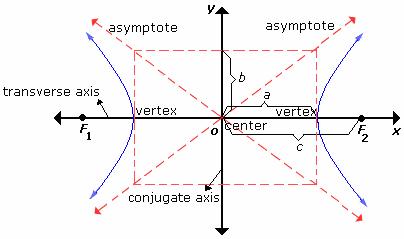
The foci of the hyperbola are (± ; c, 0).
Example of Hyperbola
Solved Example on Hyperbola
Ques: Choose the standard form of the equation for the hyperbola shown.

Choices:
Correct Answer: D
Solution:
Step 1: In the graph, 2c = 6 and 2a = 4 or c = 3, a = 2.
Step 2: c2 = a2 + b2 [Pythagorean relation.]
Step 3: 9 = 4 + b2 [Substitute 3 for c, 2 for a.]
Step 4: b2 = 5
Step 5: Since the transverse axis is horizontal, the standard form of the hyperbola is 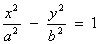 or
or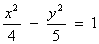 .
.
Quick Summary
- Hyperbola is defined by the difference of distances from two foci being constant.
- The general equation involves x^2 and y^2 terms with opposite signs.
- Eccentricity (e) is always greater than 1.
⚠️ Common Mistakes
- Confusing the hyperbola equation with that of an ellipse.
- Incorrectly identifying the center, vertices, and foci.
- Forgetting to consider both positive and negative branches of the hyperbola.
🌍 Real-World Uses
- Design of cooling towers in nuclear power plants which often have hyperbolic cross-sections for structural integrity and efficient airflow.
- Trajectory calculations for long-range artillery or spacecraft, where the path may be hyperbolic depending on initial velocity and gravitational forces.
- Certain lenses in telescopes use hyperbolic shapes to correct for aberrations and improve image quality.
📋 Standards Alignment
CCSS.MATH.HSG.GPE.A.3CCSS.MATH.HSG.GPE.A.2
🔗 Related Links
🍎 Teacher Insights
Emphasize the difference between hyperbola and ellipse equations. Use visual aids and real-world examples to illustrate the concept of constant difference of distances. Encourage students to practice graphing hyperbolas from different forms of the equation.🎓 Prerequisites
- Algebra
- Coordinate Geometry
- Conic Sections Basics
Check Your Knowledge
Q1: What is the standard form equation of a hyperbola with a horizontal transverse axis, centered at the origin?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the eccentricity of a hyperbola?
A: The eccentricity (e) of a hyperbola is always greater than 1 (e > 1).
Q: How do you find the asymptotes of a hyperbola?
A: The slope of the asymptotes for both horizontal and vertical hyperbolas can be found using the formula ±(b/a).